Ensure compliance and optimize financial reporting with Prima Consulting's expert IFRS 9 advisory services.
Our team helps you navigate the complexities of financial instruments and accounting standards for effective asset classification.

Our experts assess your current financial reporting framework against IFRS 9 requirements, identifying areas for improvement and implementation.
We develop a tailored implementation plan that considers your organization’s specific needs, resources, and timeline, ensuring a smooth transition to IFRS 9.
Prima Consulting builds robust ECL models aligned with IFRS 9 standards, incorporating relevant economic and industry factors for accurate credit risk assessment.
We assist in data collection, cleaning, and transformation to support ECL modeling and other IFRS 9 requirements, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
Our team supports the integration of IFRS 9 calculations into existing financial systems or recommends new solutions to meet the standard’s requirements.
We provide comprehensive training programs to enhance your employees' understanding of IFRS 9 and its implications for your business.
Prima Consulting ensures your compliance with Saudi Arabian Central Bank (SAMA) and other relevant regulatory guidelines, helping you avoid potential penalties.
We quantify the financial impact of adopting IFRS 9 on key financial metrics, providing a clear picture of its effects on your business.
Our team prepares clear and comprehensive disclosures in accordance with IFRS 9 requirements, ensuring transparency in your financial statements.
We offer ongoing support and advisory services to ensure continuous compliance and effective application of IFRS 9.
Prima Consulting offers full or partial outsourcing of IFRS 9-related functions, allowing you to focus on your core business operations.
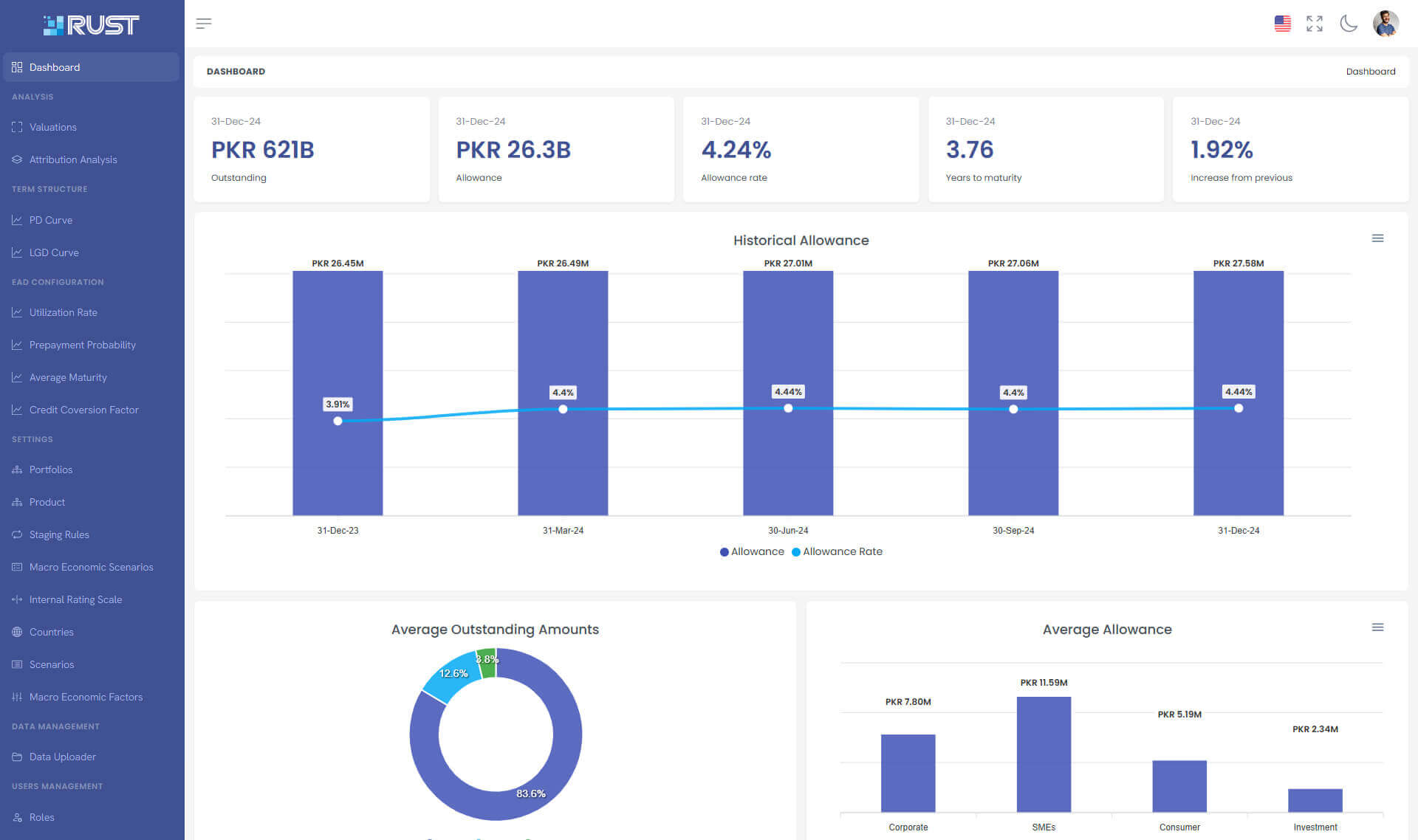
Rust IFRS 9 Software is an advanced tool specifically designed for expected credit loss modeling. It caters to banks and financial institutions by simplifying the entire process, from developing probability of default (PD) curves to managing exposure at default (EAD) and loss given default (LGD) curves.
Our team includes actuaries, financial analysts, and data specialists with over 50 years of combined experience, ensuring comprehensive solutions tailored to your needs.
We provide data-driven solutions that deliver significant time and cost reductions through efficient processes and targeted approaches.
We serve at all levels, offering strategic guidance and hands-on coaching to help you achieve success.
IFRS 9 is a complex accounting standard that governs how businesses should account for financial assets and liabilities. In simpler terms, it provides rules for determining the value of things like loans, investments, and debts on a company's financial statements. This standard aims to provide a more accurate and realistic picture of a company's financial health by requiring businesses to estimate potential losses on loans and other financial assets earlier than before. Prima Consulting's experts can guide you through the intricacies of IFRS 9 and help your business navigate this complex standard effectively.
IFRS 9 introduces a new framework for classifying and measuring financial instruments, replacing the previous IAS 39 standard. The core principle of IFRS 9 is to provide a more forward-looking approach to assessing credit risk. It requires companies to estimate potential credit losses on financial assets, such as loans and receivables, based on expected credit losses (ECL) rather than incurred losses. This means companies need to be more proactive in recognizing potential bad debts. Prima Consulting's expertise lies in helping organizations implement IFRS 9 effectively, minimizing its impact and maximizing its benefits.
The primary goal of IFRS 9 is to enhance the relevance and reliability of financial information presented in financial statements. By introducing a forward-looking approach to credit risk assessment, IFRS 9 aims to provide a more accurate picture of a company's financial position. This standard seeks to improve the comparability of financial information across different entities by establishing clear and consistent principles for classifying and measuring financial instruments. Ultimately, IFRS 9 is designed to better inform investors and creditors about a company's financial health and risks.
IFRS 9 is built on three core principles: classification and measurement, impairment, and hedge accounting. The classification and measurement principle determines how financial assets and liabilities are categorized and valued. The impairment principle focuses on assessing the credit risk associated with financial assets and recognizing expected credit losses (ECL). Hedge accounting provides rules for managing financial risks through hedging instruments. These principles work together to ensure a more accurate and forward-looking representation of a company's financial position. Prima Consulting can assist your organization in understanding and implementing these principles effectively.
IFRS 9 categorizes financial assets into three main categories based on the business model for managing the asset and the contractual cash flow characteristics:
ECL = EAD * PD * LGD — Calculating Expected Credit Losses (ECL) under IFRS 9 involves a complex process that considers various factors, including the probability of default, loss given default, and exposure at default. The ECL calculation is based on a forward-looking assessment of credit risk. There are different approaches to calculating ECL, including the simplified approach and the general approach. Prima Consulting's experts can assist you in selecting the appropriate ECL model and implementing the calculation process effectively.
IFRS 9 was introduced to address the limitations of the previous IAS 39 standard. The primary need for IFRS 9 arose from the desire for a more forward-looking and relevant approach to financial reporting. By requiring earlier recognition of expected credit losses, IFRS 9 provides a more accurate representation of a company's financial health and risk profile. Additionally, the standard enhances the comparability of financial information across different entities. Ultimately, IFRS 9 aims to improve the quality and usefulness of financial statements for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
The IFRS 9 ECL model is a central component of the standard, requiring entities to estimate and recognize expected credit losses on their financial assets. This model replaces the incurred loss model used under IAS 39. The ECL model promotes a more prudent approach to credit risk management by forcing companies to anticipate potential losses rather than waiting for them to occur. Prima Consulting can assist you in developing and implementing a robust ECL model tailored to your organization's specific needs.
IFRS 9 has had a significant impact on the banking industry. The standard introduces a new impairment model based on expected credit losses, requiring banks to be more proactive in assessing the creditworthiness of their loan portfolios. This has led to increased provisioning and a potential impact on profitability. Additionally, IFRS 9 affects the classification and measurement of financial instruments, such as derivatives and trading assets. Prima Consulting has deep expertise in the banking industry and can help banks navigate the complexities of IFRS 9 implementation.
IFRS 9 introduced significant changes to hedge accounting compared to IAS 39. The most notable difference lies in the approach to hedge effectiveness testing. Under IAS 39, hedge effectiveness was determined through rigorous quantitative tests, often leading to complexities and inefficiencies. IFRS 9 adopts a more principles-based approach, focusing on the economic relationship between the hedging instrument and the hedged item. This allows for greater flexibility in hedge accounting while maintaining the integrity of the hedge relationship. Additionally, IFRS 9 expanded the scope of eligible hedging instruments and introduced new hedge designations, providing more options for risk management strategies.
While both IAS 39 and IFRS 9 deal with financial instruments, IFRS 9 represents a significant overhaul of the previous standard. One of the most fundamental differences lies in the impairment model. IAS 39 used an incurred loss model, recognizing credit losses only when they were evident, often leading to delayed recognition of financial distress. In contrast, IFRS 9 adopts a forward-looking expected credit loss (ECL) model, requiring entities to estimate potential credit losses based on current information and economic conditions. This shift promotes a more prudent approach to risk management. Additionally, IFRS 9 introduced changes to classification and measurement, hedge accounting, and other areas, aiming to provide more relevant and reliable financial information.
Your Trusted Partner for Financial & Risk Management Solutions in the MENA Region